- Home >
- Education Center >
- Fundamentals of CO2 Arc Welding >
- Fundamentals of MAG Welding (CO2 Arc Welding) >
Fundamentals of MAG Welding (CO2 Arc Welding)
10. Influence of wind velocity
In gas−shielded arc welding like CO2 arc welding, poor shielding effect tends to generate blowholes. Be sure that the shielding effect deteriorates especially when it is windy.
Fig. 6 shows an example of the X−ray test results of the weld bead deposited on a 9−mm thick plate. It exhibits that there is a sharp increase of blowholes when the wind is over 2m/sec. in velocity.
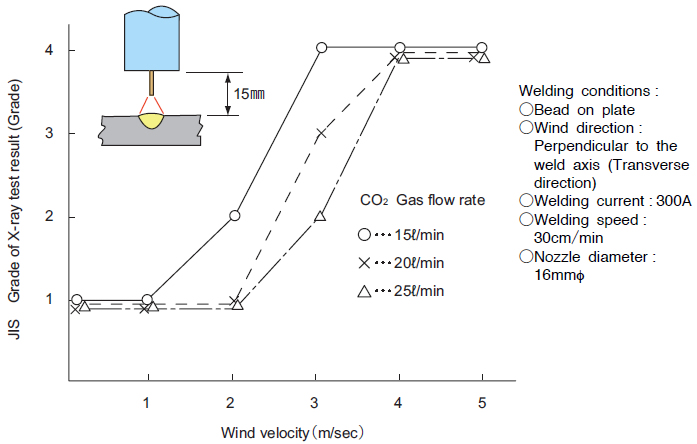
Fig. 6 Example of X−ray test results
In order to prevent blowholes, it is recommended to use partitions or windbreak screens for protective measures. Also, in order to get more efficient shielding, it is important to shorten the distance between the contact tip and the base metal and to increase the gas flow rate in the respective allowable ranges.

11. Weld imperfections and preventive measures
| Weld imperfections | Causes (Preventive measures) |
|---|---|
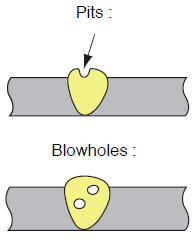 |
1 Shortage of CO2 gas flow rate. 2 Gas heater does not work. 3 Purity of CO2 gas is not enough. 4 Inadequate gas shielding. 5 Excessive nozzle standoff distance. 6 Much oil or grease is deposited on the base metal. 7 Much scale is remained on the base metal. 8 Much rust is remained on the base metal. 9 The shielding nozzle is clogged with much spatter. 10 Too long arc length (Too high arc voltage). |
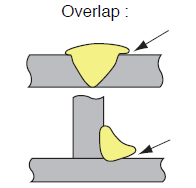 |
1 Too low welding current. 2 Too high welding current. 3 Too low arc voltage. 4 Too low welding speed. 5 Wrong targeting position of the welding wire. 6 Too small groove angle. |
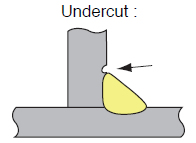 |
1 Too high arc voltage. 2 Too high welding current. 3 Wrong targeting position of welding wire. 4 Rough manipulation of the welding torch. 5 Too high welding speed. |
| 1 The center of the wire feed roller is deviated. 2 Inappropriate adjustment of the wire straightener. 3 Loosened contact tip. |
|
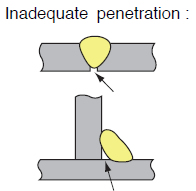 |
1 Too low welding current. 2 Too low arc voltage. 3 Too high arc voltage. 4 Too low welding speed (in groove welding) 5 Too high welding speed. 6 Too narrow groove angle. 7 Wrong targeting position of the welding wire. |
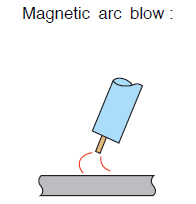 |
1 Too large tack weld. Or, welding is directed towards the preceding weld. 2 Place the workpiece cable connection away from the weld as far as possible (on a large weldment). 3 On a small weldment, place the workpiece cable connection at the start of the weld. 4 Keep the arc length shorter 5 Direct the welding torch toward the opposite direction of the magnetic arc blow. 6 Put tab plates at both the start and end of the weld line. *2~6:Preventive measures |
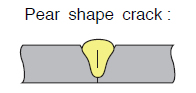 |
1 Too high welding current. 2 Too narrow groove. 3 Too low arc voltage. 4 Wrong targeting position of the welding wire. |
| 1 Too large contact tip diameter for the wire diameter used. 2 Worn contact tip. 3 Loosened contact tip. 4 Irregular rotation of the wire reel. 5 Worn groove of the wire feed roller. 6 Inadequate pressure of the pressure roller. 7 Large resistance of the conduit tube. 8 Too long wire extension. 9 Too low or high arc voltage. 10 Too low welding current. 11 Inappropriate welding speed. 12 Unstable torch manipulation. 13 Nozzle is clogged with much spatter. 14 Fluctuation of wire extension. 15 Wrong targeting position of the welding wire. 16 Contaminated base metal with dirt such as rust, paint and oil. 17 The position of the workpiece cable connection is inappropriate. |






