- Home >
- Education Center >
- Welding References >
- Welding terminology >
Welding References
1-4. Welding terminology
Welding terminology is specified by the JIS standard (Z 3001−1999). Shown below are the typical ones. (Refer to A3.0 for the AWS standard.)
| Technical term | Definition |
|---|---|
| deposited metal test specimen |
A test specimen with all−deposited−metal testing section. |
| root bend specimen | A butt weld joint bend specimen whose root side is bent in tension. |
| face bend specimen | A butt weld joint bend specimen whose surface side is bent in tension. |
| side bend specimen | A bend specimen for testing the weld cross section. |
| guided bend test | A bending test in which the specimen is bent to a definite shape by using a set of male and female dies. |
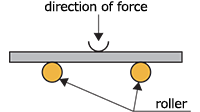
| roller bend test | A bending test in which the specimen is placed across the supports of rollers as shown in the figure below and is bent by the force of plunger.
 |
| free bend test | A bending test in which the lengthwise ends of a specimen are bent to an initial angle and then the specimen is bent freely by applying forces on both of the ends without using a set of male and female dies or aset of rollers. |
| multi−layer welding | A weld consisting of multiple layers of beads. |
| pit | A small hole occurred in the weld surface. |
| surfacing | A welding technique to lay a desired deposited metal on ametal surface. |
| hardfacing | A welding technique to lay a hard deposited metal on a metal surface. |
| notch brittleness | Even if a particular metal has sufficient ductility when it contains no notch, the metal can be brittle to become fractured when it contains a notch. Such a brittle characteristic is referred to as notch brittleness. |
| crater | A depression in the weld surface at the termination of an arc weld bead. |
| residual stress | Stresses remained in a structure or its component. |
| crack sensitivity | Easiness of weld cracking. |
| weldability | The welding suitability of the base metal quality. |
| consumable nozzle electroslag welding |
An electroslag welding process that uses a consumable nozzle. |
| spring contact arc welding | An arc welding process in which a dedicated electrode is kept contact at a certain low angle with respect to the welding line during welding by using the spring force of the dedicated device placed on the weldment. |
| one−side welding | A butt joint welding variation in which the welding is completed from the single−groove side of the joint makingamelt−through weld with a backing material. |
| Technical term | Definition |
|---|---|
| welded joint | A joint welded. |
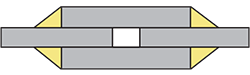
| strapped joint | A lap joint variation in which the thickness−wise surfaces of splice plates are fillet welded with the surface of the components to be joined.
 |
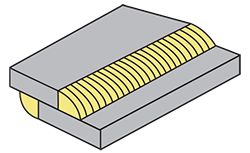
| lap joint | A weld joint variation in which two members are partly overlapped to fillet weld one member’s surface and the other member’s thickness−wise surface.
 |
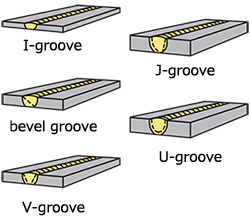
| single groove joint | A weld joint variation in which a single groove is prepared on the one−side surface of the members to be joined ; the basic groove shapes are as follows.
 |
| double groove joint | A weld joint variation in which double grooves are prepared on double−side surfaces of the members to be joined ; the basic groove shapes are as follows.
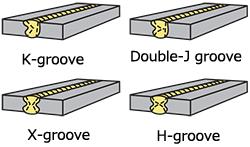 |
| joggled lap joint (Offset lap joint) |
A lap joint variation in which one member’s edge is formed with joggling to make the two members aligned in the same plane, which is also known as offset lap joint.
 |
| edge joint | A weld joint between the edges of two or more parallel or nearly parallel members.
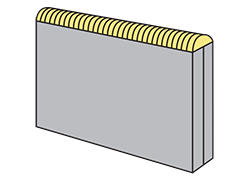 |
| butt joint | A weld joint between two members aligned approximately in the same plane. |
| corner joint | A weld joint between two members located approximately at right angles to each other in the form of an L, the corner of which is welded.
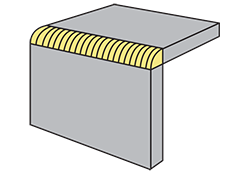 |
| tee joint | A weld joint between two members located approximately at right angles to each other in the form of a T, in which one member’s edge is put on the other member’s surface.
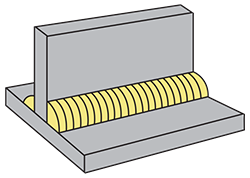 |
| welding groove | A groove prepared between two members to be welded ; the typical grooves are as follows.
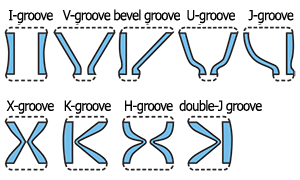 |
| groove angle | The total included angle of the groove between two parts to be joined by a groove weld.
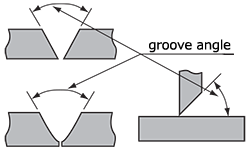 |
| bevel angle | The angle formed between the prepared edge of a member and a plane perpendicular to the surface of the member.
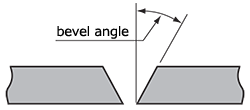 |
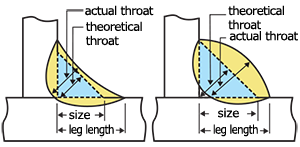
| leg length | The distance from the root of the joint to the toe of the fillet weld.
 |
| size of fillet weld | The size of fillet weld (S1, S2, S3) is specified for designing the weldment. The triangle determined with the sizes must be inscribed within the fillet weld cross section.
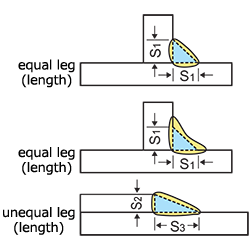 |
| actual throat, (actual throat of fillet weld), (actual throat of butt weld) |
For a fillet weld, the shortest distance, measured in its cross section, from the root of weld to its face. For a butt weld, the smallest thickness measured through the root of weld in its cross section.
 |
| throat | Refer to theoretical throat and actual throat. |
| theoretical throat, (theoretical throat of fillet weld), (theoretical throat of butt weld) |
For a fillet weld, the distance from the root of the joint perpendicular to the hypotenuse of the right triangle determined with the fillet weld sizes. For a butt weld, the thickness of the components to be joined. When the components have different thicknesses, the thinner one is taken as the theoretical throat. |
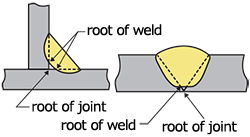
| root of weld | In the cross section of a weld, the points at which the bottom of the weld intersects the base metal. |
| root of joint (root of butt welded joint), (root of fillet welded joint) |
For butt welding, that portion of a joint to be welded where the members approach closest each other. For fillet welding, that portion of a joint to be welded where two members intersect each other.
 |
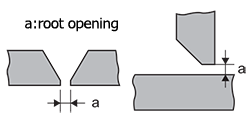
| root opening (root gap) | The separation between the members to be joined at the bottom of the welding groove.
 |
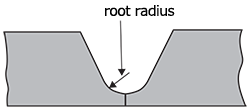
| root radius | The radius of the bottom of a J−,U−, and H−groove.
 |
| root face | The upright face at the bottom of a welding groove.
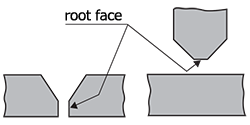 |
| weld toe | The junction between the face of weld and the base metal.
 |
| welding symbol | A symbolic representation of welds on drawings. |
| fillet welded joint | A joint welded by fillet welding. |
| cruciform joint (cross shaped joint) |
A joint welded by fillet welding the members assembled to a cross shape as shown in the figure below.
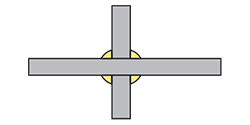 |
| groove depth | The distance from the surface of a base metal to the bottom of the welding groove prepared between two members to be joined.
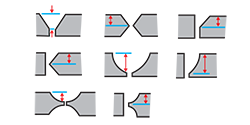 |
| groove face | That surface of a member included in the groove for welding. |
| scarf joint | A joint variation in which the members to be joined are prepared with single−bevel edges arranged with parallel groove faces to create a wide faying surface, which is used mainly for brazing and forging. |
| Technical term | Definition |
|---|---|
| weaving | A type of welding manipulation in which the electrode is oscillated transversely as the welding is progressed. |
| backing | A technique to support molten metal by placing a metal or a refractory against the backside of the weld. |
| backing strip | A metallic strip for backing. |
| back chipping | The removal of weld metal and base metal from the backside of a butt welded joint to remove incomplete penetration or the root pass weld to assure complete penetration upon subsequent welding from that side. |
| magnetic arc blow (Arc blow) |
The deflection of an electric arc from its normal path because of electromagnetic force. |
| layer | A layer of weld metal consisting of one pass or multiple passes |
| pass (run) | A single welding operation in the progression direction along a joint. |
| overhead position | The position in which welding is performed from the underside of a joint whose weld axis and face are kept in almost horizontal.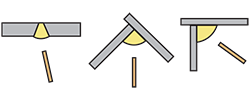 |
| horizontal position | The position in which welding is performed from the lateral side of a joint whose weld axis is kept in almost horizontal and, for butt welding, the weld face is kept in almost vertical.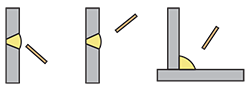 |
| vertical position | The position in which welding is performed from the face of a joint whose weld axis is kept in almost vertical.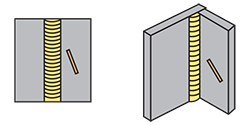 |
| flat position | The position in which welding is performed from the top side of a joint whose weld axis and face are kept in almost horizontal.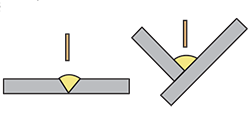 |
| welding line | The line showing the direction of a bead, fillet weld, or butt weld. |
| welding current | An electric current to generate a heat needed for welding. |
| weld length | The length of a continuous weld excluding its start and crater portions. |
| effective length of weld | The entire length of a weld, throughout which the intended−size cross section exists. |
| penetration (weld penetration) |
The largest distance the weld metal extends from the surface of the base metal or the groove face.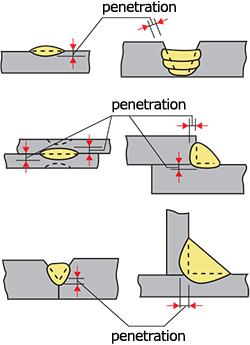 |
| weld reinforcement | Weld metal in excess of the size required for a groove weld or a fillet weld.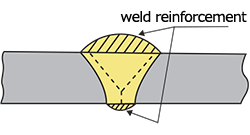 |
| undercut | A groove melted into the base metal adjacent to the weld toe or weld root and left unfilled by weld metal.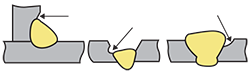 |
| overlap | The protrusion of weld metal beyond the weld toe or weld root, which is not fused with the base metal.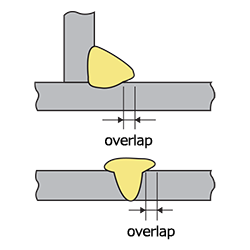 |
| fisheye | A fisheye−like area of silver gray in color, which may appear in the fracture surface of a weld metal. |
| slag | A nonmetallic product generated on a weld. |
| slag inclusion | A discontinuity consisting of slag entrapped in weld metal or at the weld interface. |
| spatter | The metal or slag particles expelled during arc welding and oxyfuel gas welding. |
| spatter loss | Metal loss due to spatter. |
| blowhole | Cavity type discontinuities formed by gas entrapment in the weld metal during solidification. |
| underbead crack | A crack occurred generally in the heat−affected zone, near the bead, which generally not extends to the surface of the base metal. |
| deposition rate | The mass of deposited metal in a unit of time. |
| deposition efficiency | The ratio of the mass of deposited metal to the net mass of welding consumables consumed, exclusive of stubs. For covered electrodes, the mass of its covering is included normally, but excluded for a specific purpose. |
| weld bead | A weld resulting from a weld pass. |
| melting rate | The mass or length of electrode, wire, or rod melted in a unit of time. |
| weld pool (molten pool) | The depressed local area of molten metal due to the welding arc heat. |
| preheating | The heating of the base metal prior to welding or oxyfuel gas cutting. |
| postheating (immediate postheating, postweld heat treatment) |
The application of heat to an assembly after welding or oxyfuel gas cutting. The postheating that is applied to an assembly immediately after welding to remove diffusible hydrogen from the weld and to prevent cold cracking is called as “immediate postheating.” The postheating that is applied to an assembly after welding to remove residual stresses and to improve mechanical properties and corrosion resistance is called as “postweld heat treatment.” |
| weld metal zone | That portion of the weld area that was fused and solidified. |
| deposited metal | The metal that has been deposited on the base metal by welding with a filler metal. |
| weld zone (weld) | The general term for the weld metal plus the heat−affected zone. |
| weld metal | Metal included in a weld that was fused and solidified during welding.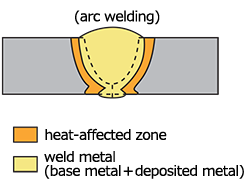 |
| heat−affected zone | The portion of base metal that was not melted but its mechanical properties and microstructure have been altered by the heat of welding or thermal cutting. |
| convex fillet weld | Fillet welds having a convex weld face.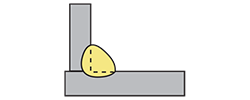 |
| concave fillet weld | Fillet welds having a concave weld face.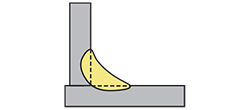 |
| continuous fillet weld | A fillet weld with a continuous weld length. |
| slot weld | A weld made in an elongated hole in one of the two lapped members of a joint. |
| plug weld | A weld made by filling a circular hole with a filler metal in one member of a joint, fusing that member to another member.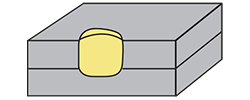 |
| flare groove weld | A weld made in the flare groove of two members of a joint. |
| butt weld | A weld made in a butt joint. |
| seal weld | Any weld intended only to provide a specific degree of tightness against leakage of a liquid. |
| buildup welding | A surfacing variation in which surfacing material is deposited to achieve the required dimensions on a substrate that is worn or lacking in dimension. |
| buttering | A surfacing variation that deposits a dissimilar metal on the groove surface of a base metal to prevent the chemistry effect of the base metal on the weld metal that is to be deposited subsequently by butt welding. |
| underlaying | A surfacing variation that deposits a low−crack−sensitive metal to prevent cracking or disbonding prior to the buildup welding on the base metal. |
| scallop | A fan−shaped opening made in a member to avoid crossing the welding line of the member with that of another associated member.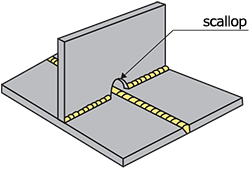 |
| back run | A weld made at the back of a single groove weld, which is laid after the face side welding. |
| backing weld | A backing variation in which a weld is laid on the backside of a groove in advance to prevent excessive melt−through in the arc welding of the face side. |
| groove weld | A weld made in a groove. Typical groove weld variations are shown in the following. I−groove weld, V−groove weld, Single−bevel groove weld, U−groove weld, J−groove weld, X−groove weld, H−groove weld, K−groove weld, Double−J groove weld. |
| backhand welding | A welding technique in which the welding torch is directed opposite to the progress of welding. |
| forehand welding | A welding technique in which the welding torch is directed toward the progress of welding. |
| tack welding | A welding variation in which a weld is made to hold the parts of a weldment in proper alignment until the main welds are made. |
| skip welding | A welding technique in which intermittent welds are laid first and then the skipped areas are welded after the intermittent welds are cooled sufficiently, the main purpose of which is to minimize welding distortion. |
| fillet weld | A weld of approximately triangular cross section jointing two surfaces approximately at right angles to each other in a lap joint, T−joint, and corner joint. |
| front fillet weld | A fillet weld variation in which the fillet weld axis is almost normal to the direction of applied shear stresses. |
| side fillet weld | A fillet weld variation in which the fillet weld axis is almost parallel to the direction of applied shear stresses. |
| intermittent fillet weld | A weld in which the continuity is interrupted by recurring unwelded spaces. |
| staggered intermittent fillet weld | An intermittent fillet weld on both sides of a T−joint in which the weld increments on one side are alternated with respect to those on the other side.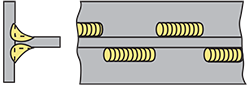 |
| backstep welding | A welding technique in which the electrode manipulation direction for each pass is opposite to the entire progress of welding.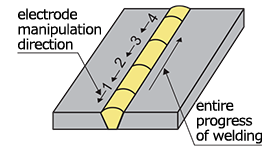 |
| block sequence (block welding) |
A deposition sequence variation for a multi−pass weld in which separated increments are welded with several layers before intervening increments are welded.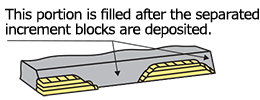 |
| boxing | The continuation of a fillet weld around the corner of a member as an extension of the principal fillet weld.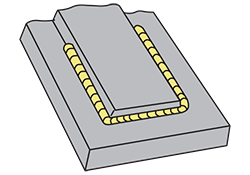 |
| weld tab, runoff weld tab (run−off plate), starting weld tab (run−on plate) |
Additional material that extends beyond either end of the joint, on which the weld is started on the starting weld tab or terminated on the runoff weld tab. |
| burn−through (excessive melt−through) |
Dropping of molten metal to the opposite side of a groove through the root of the joint. |
| preset distortion | The artificial angular distortion provided in a base metal toward the reverse direction before welding to an extent which is expected to be induced by the face side welding. |
| gravity welding | A shielded metal arc welding variation in which a covered electrode is held by the dedicated device, and the welding is progressed automatically as the holder slides down by the gravity while the electrode consumes contacting to the welding line and keeping a certain angle with respect to the base metal. |
| arc striking | To initiate an arc or to generate it momentary on a base metal followed by immediate putting out. |
| Technical term | Definition |
|---|---|
| AC arc welding. | A welding variation in which AC current is used to generate an arc. |
| DC arc welding. | A welding variation in which DC current is used to generate an arc. |
| automatic arc welding | Arc welding with equipment in which welding wire is fed automatically and the welding is progressed continuously without manual control. |
| semiautomatic arc welding | Arc welding with equipment which controls the welding wire feed while the welding torch is manipulated manually. |
| electrode negative | The arrangement of direct current arc welding leads in which the electrode is the negative pole and the workpiece is the positive pole of the welding arc. |
| electrode positive | The arrangement of direct current arc welding leads in which the electrode is the positive pole and the workpiece is the negative pole of the welding arc. |
| arc voltage | A voltage supplied between both poles of an arc. |
| arc length | The distance between both poles of an arc. |
| workpiece cable connection | The electrical connection of the workpiece cable with a base metal or other metallic body to which the base metal contacts. |
| exposed core | The uncoated part of a covered electrode for holding with a electrode holder. |
| consumable electrode | An electrode that is fused and consumed in the arc during arc welding and arc cutting. |
| non−consumable electrode | An electrode that is hard to be consumed by the arc heat due to high melting point. |
| electrode diameter | The diameter of the core wire of a covered electrode. |
| droplet | Molten metal particles that transfer from the tip of the welding electrode to the base metal. |






