- Home >
- Products >
- Technical Highlight >
- Vol.23: THE KOBELCO ARC over the Last Decade
Technical Highlight Vol.23
Vol.23: THE KOBELCO ARC over the Last Decade

The swing from active to sluggish market(2008 ~ 2010)
In the years leading up to 2008, the world economy remained strong, thanks to booming economic growth in developing nations, including China. These trends were mirrored in the welding industry, and demand for welding consumables in the shipbuilding and energy industries increased. Due to increasing demand for crude oil and other natural resources, commodity prices continuously increased, leading to ever more construction of such facilities as offshore structures for exploration and production of oil or natural gas as well as crude oil tankers,storage tanks and oil refineries. Indeed, many industries that enrich human lives prospered, including automobiles and construction of power plants, infrastructure and commercial and residential buildings.
In many industries, demand increased not only for welding consumables but also for greater production capacity and automated production systems, and KOBELCO was in good position to supply both. Having developed and supplied automatic welding technologies to Japanese shipyards and related industries since the 1970s, KOBELCO now supplied them to new overseas markets.
These exports included RF™ (Figure 1) and FCB™ (Figure 2) equipment for one side welding processes long utilized in Japanese shipyards for panel joining; processes such as SEGARC™ (Figure 3), for automatic vertical welding of heavy plates, and TRIFARC™ (Figure 4), which allows highly efficient horizontal fillet welding; and the ARCMAN™ robotic welding systems for construction machinery and steel frame construction. Used together with exclusively-developed welding consumables, these technologies delivered superb performance within their respective circumstances.

Figure 1: RF™ equipment for one side welding

Figure 2: FCB™ equipment for one side welding

Figure 3: Welding site of SEGARC™ process

Figure 4: Welding site of TRIFARC™ process
However, following the Beijing Olympic and the financial crisis caused by the subprime mortgage problem, this favorable business climate cooled. Enthusiasm for investment slowed, resource prices dropped, and the world economy quickly went into recession. However, while at first it seemed the adjustment phase would last long, the world economy slowly began showing signs of recovery in 2010, thanks to continued growth in the BRICS and other developing nations.
Around this time, the following new trademarks were adopted for KOBELCO’s welding consumables:
TRUSTARC™: ( “TRUST”+“ARC” ) is used for 590MPa or higher tensile strength steel, low temperature and heat resistant steels.
PREMIARC™: ( “PREMIUM”+“ARC” ) is used for high alloy steel, stainless steel and non-ferrous metal.
In 2008, the new trademarks were incorporated into new product names; for example, RB-26 became FAMILIARC™ RB-26; CMA-106 became TRUSTARC™ CM-A106; and DW-308LP became PREMIARC™ DW-308LP.
One of the above trademarks is displayed on each KOBELCO welding consumable. In this article, the trademarks will be abbreviated as [F],[T], and [P], respectively.
The re-emergence of developing nations(2011 ~ 2013)
In March 2011, the Great East Japan Earthquake and the tsunami that followed caused unprecedented damage. The Japanese economy that had been suffering in the aftermath of the financial crisis was damaged further. Many scars still remain.
By contrast, while instability caused by the European and American debt problems hampered the recovery of the world economy, easy-money policies and economic stimulus measures implemented in many countries resulted in an expansion of demand, increased prices for energy and natural resources, and an upturn of business worldwide.
As in the years prior to 2008, the oil and gas industries grew significantly. Construction of offshore structures, oil refineries, ships and ship-related buildings boomed, particularly indeveloping countries. Fabricators in both industrialized countries and developing nations saw their orders rise.
Once again, KOBELCO’s efficient and time-tested welding technologies attracted customers while at the same time the company introduced new product lines and high value-added products into the market. For example, new products for pipeline construction included [T]DW-A70L, which offers stable mechanical properties and excellent workability for welding API 5L X80; [P]DW-N625P for all position welding of clad pipes; and flux cored wires (FCWs) for pipes under sour gas environments. Other new product lines were developed for low temperature services. The welding consumables for 9%Ni steels, used in Japan to construct natural gas storage tanks and transportation equipment, seemed to meet the needs of the times as their use spread widely in many regions.
On the other hand, this period also saw increasing consolidation in the welding industry, through M & A and other trends, due to an expectation of long-term unstable demand. However, even under such trying circumstances, KOBELCO continued to sell consumables, by meeting market needs and offering unique technical capabilities, and introduced new product lines developed for a range of industries. This is the well-known and renowned “KOBELCO Way.”
The challenge of new environments(2014 ~ 2017)
In the second half of 2014, weak demand in developing nations helped trigger a decrease in worldwide energy demand, leading to a drop in crude oil prices that had exceeded 100 US$/barrel. With North American shale gas production adding to the glut, the fall in oil prices was sharp and swift. Even in 2017, crude oil prices remained low at about 50 US$/barrel, as advancements in drilling technologies ensured further cost reductions in shale gas production. The prices of other resources followed nearly the same path. In many places, regional conflicts as well as corruption and scandals accelerated economic stagnation. As a result, fiscal austerity measures were introduced in many countries, causing even more instability.
On the other hand, in Japan, the easy-money policy as well as demand for construction in response to earthquake damage and preparation for the Tokyo Olympics helped to improve employment and corporate performance. However, long lasting deflationary concerns were not dispelled due to uneasiness about the future. Despite demand in the short term, the declining birthrate and aging society have meant that high efficiency and manpower saving have become essential on a long-term basis.
KOBELCO’s robotic welding technologies, developed over the years with corresponding welding consumable, are expected to play an important role. The ARCMAN™ series of welding robots and CB-type controllers are now capable of high quality welding on medium-thick to heavy plates and offer excellent operability. In addition, the digitally controlled SENSARC™ AB500 welding power source provides highly efficient tandem welding, and the REGARC™ process (Figure 5) enables low spattering and efficient GMAW even with CO2 shielding gas by controlling the welding current and arc voltage waveforms.
These technologies have been applied not only in Japan but also in overseas regions where construction demand is high, such as North America, East Asia, Southeast Asia, and South Asia. Even in the field of shipbuilding, the need for automation was so high that a robotic welding system for hull assembly (Figure 6) was developed and applied in 2017 for the first time. KOBELCO’s strengths lie in supplying total welding solutions to users with particular needs in a diverse range of industries.

Figure 5: Welding site of REGARC™ process

Figure 6: Application of robotic welding system for hull assembly in shipbuilding
KOBELCO’s recent history overseas ---- China ----
In China, KOBELCO increased sales of welding consumables and equipment by meeting local needs when demand for construction and energy rose during the build up to such large-scale events as the Beijing Olympics in 2008 and the Shanghai World Expo in 2010.
Since KOBE WELDING OF TANGSHAN CO., LTD. (KWT) (Figure 7) was established as a production base of solid wires in 2002 (Figure 8), it has contributed to the operations of customers, especially car and construction machinery manufacturers.

Figure 7: KWT factory appearance

Figure 8:KWT’s product rang+es
Japanese-affiliated as well as local producers have given high marks to [F]MG-51T for thin plates and [F]MG-50CH for heavy plates. As a producer of highly reputed solid wires in pail-packs for automatic welding, such as the large-sized ARROW PACK, KWT was able to increase packed wire production lines when demand for automatic welding increased. Also popular with customers have been the SE series solid wires with no-Cu coating (Figure 9) that are exported from Japan and feature smooth wire feeding and a reduced environmental load.
In order to keep up with the growing shipbuilding industry and to manufacture made-in-China welding consumables for shipyards, KOBE WELDING OF QUINDAO CO., LTD. (KWQ) (Figure 10) was established as a supply base of FCWs in 2008. Since then it has been contributing to development of local industries. The range of products manufactured in KWQ (Figure 11) has been expanded to meet the users’ needs, including FCWs for low temperature services.

Figure 9:SE series solid wires

Figure 10: KWQ factory appearance

Figure 11: KWQ’s product ranges
KOBELCO’s sales organizations have been reorganized to respond to the diverse needs in the Chinese market. In 2010, KOBE WELDING OF SHANGHAI CO., LTD. (KWSH) (Figure 12) was established as a sales company, and in 2014, a China KOBELCO “Shin-Yo-Kai” (sales and distribution network) (Figure 13) was organized in the same manner as those in Japan and Thailand, which have proven to be successful over the years. The “Shin-Yo-Kai” networks are an effective means of supplying KOBELCO consumables and providing customer service. In China, they responded to demand from energy-related projects for consumables for Cr-Mo-V steels applied in petro-chemical reactors as well as for consumables for LNG-related plants and crude oil storage tanks. The networks also support local users’ Monodzukuri (production system innovation) and, as such, are highly appreciated.

Figure 12: Entrance of KWSH

Figure 13: China-KOBELCO “Shin-Yo-Kai”
KOBELCO meets the needs of regional users with local production of welding consumables that are expected to increase in demand.
KOBELCO’s recent history overseas ---- Korea ----
Although the Korean economy fell temporarily due to the financial crisis stemming from the subprime mortgage problems, it recovered quickly as local fabricators enjoyed increased demand from the shipbuilding and energy sectors, which resulted in more demand for welding consumables as well. Because of the rise of Chinese manufacturing, Korean manufacturers shifted production into more value added products. For example, large shipyards took on orders for offshore structures, like FPSO’s as well as the world’s first FLNG; accordingly, demand increased for high value added welding consumables, such as those for low temperature services and for high tensile steels.
KOBELCO’s local production base, “KOBE WELDING OF KOREA CO., LTD. (KWK) (Figure 14), expanded its production menu (Figure 15) according to changing demand from users. For example, with increased construction of offshore structures and LNG storage tanks, inquiries increased for consumables for high performance steels like 9%Ni and Ni-based alloys; indeed, a range of KOBELCO products and technologies were supplied as well. KWK celebrated the 20th anniversary of its founding in 2015 and will continue supplying high and stable quality products.

Figure 14: KWK factory appearance

Figure 15: KWK’s product ranges

Figure 16: Entrance of KWMK
In order to catch the market needs of front-line manufacturers and to contribute to their Monodzukuri, the sales company, KOBELCO WELDING MARKETING OF KOREA CO., LTD. (KWMK) (Figure 16) was established in 2012 for better distribution of high quality consumables. Although demand for new sources of energy is presently stagnant due to sluggish crude oil prices, KOBELCO continues to watch the markets in order to meet customer needs with the supply of consumables at any time.
KOBELCO’s recent history overseas ---- Southeast Asian (ASEAN) Countries ----
It is in the ASEAN regions where KOBELCO has been doing business for decades. There are two production bases in Thailand: THAI-KOBE WELDING CO., LTD. (TKW), which was established nearly 50 years ago, and KOBE MIG WIRE (THAILAND) CO., LTD. (KMWT), which celebrated its 25th anniversary in 2009. Both TKW and KMWT (Figure 17) reaffirmed their determination to continue supplying high quality products matching regional needs (Figure 18). In 2011, a major flood severely damaged local users, including Japanese-affiliated companies, and disrupted worldwide supply networks, particularly of Japanese car manufacturers. As KOBELCO’s resident companies in Thailand, TKW and KMWT experienced the hardship with the people and made a donation toward reconstruction.

Figure 17: TKW/KMWT factory appearance

Figure 18: TKW/KMWT’s product ranges
In Singapore, the well-established KOBE WELDING (SINGAPORE) PTE. LTD. (KWS) celebrated its 30th anniversary in 2009. However, in 2012, it was reorganized as KOBELCO WELDING ASIA PACIFIC PTE. LTD. (KWAP) (Figure 19), taking responsibility for the whole ASEAN region. The ASEAN OPERATIONS DIVISION was set up at KWAP to oversee sales, marketing and R & D in not only Singapore but also the other ASEAN countries. It also collects information on needs from outside the region and performs the tasks necessary for the development and supply of new products. Low hydrogen electrodes manufactured at KWAP had long been utilized by offshore structure fabricators and shipyards in Singaporean and neighboring countries. However, as these users began to apply higher grade steels, including those for low temperature services, KWAP added [T]LB-52NS to its manufacturing line-up and even installed more vacuum packing units (Figure 20) to meet the increased demand.

Figure 19: KWAP factory appearance
![Figure 20: Vacuum packed [T]LB-52NS](../../images/education-center/technical_hightlight/vol23_21.png)
Figure 20: Vacuum packed [T]LB-52NS

Figure 21: KWM factory appearance
In Malaysia, KOBE WELDING (MALAYSIA) SDN. BHD. (KWM) (Figure 21) was reorganized from ST KOBE Company and restarted sales of [F]RB-26, an older but well-regarded product, as well as other covered electrodes in response to the needs of customers in the region.
In Vietnam, the Representative Office was set up in 2012 in order to perform community-based activities. Information about local needs, gained through the office, is fed back to our R & D engineers. KOBELCO welding consumables including [F]RB-26 and LB type low hydrogen covered electrodes, manufactured in Thailand and/or Singapore, have been exported to and favorably accepted in such surrounding countries as Myanmar, Cambodia, Laos, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
2017 marked 40 years since P.T. INTAN PERTIWI INDUSTRI (INTIWI) (Figure 22) and KOBELCO began technical collaboration in Indonesia. INTIWI manufactures KOBELCO products under license and sells them as well as other KOBELCO consumables to meet local demand. In this way, INTIWI contributes to the country’s industrial development and will do so in the future as well.
Wherever it operates, KOBELCO always considers the relationship with local partners or distributors to be most important. For example, the Thailand “Shin-Yo-Kai” (sales and distribution network) meets periodically in order to reconfirm mutual relationships, assess the distribution of KOBELCO products to users, and reflect upon the unity of the organization in its contribution to the development of the industries it serves with products and technical services. The ASEAN “Shin-Yo-Kai” (Figure 23) meets every several years to accomplish similar goals throughout the region.

Figure 22: INTIWI factory appearance

Figure 23: ASEAN “Shin-Yo-Kai”
Southeast Asia is a growing market. Although construction of offshore structures and energy-related projects is currently slow, general construction remains healthy. KOBELCO will keep on proposing total welding solutions including automation that respond to the needs of customers in the region.
KOBELCO’s course of history in the world ---- India and the Middle East ----

Figure 24: Entrance of KWI
One of the five rapidly-growing BRICS countries, India is a market in which KOBELCO consumables maintain a strong position in energy and construction projects. Our consumables for heat resistant steels, which are essential for boilers used in thermal power generation, have long been highly reputed by Indian fabricators. In order to maintain a close relationship with local partners and users, KOBELCO WELDING INDIA PVT. LTD. (KWI) (Figure 24) was established in a suburb of New Delhi in 2011. Responding to an inquiry for automation, KWI introduced a robotic welding system. KOBELCO’s technology on robotic welding, accumulated and cultivated over many years, will play an important role in raising the production efficiency of construction machinery and penstocks, which are essential for continued growth of the Indian economy.
In the Middle East, increased demand for energy has led to a boom in construction projects - - and thus increased sales of applicable welding consumables. KOBELCO’s covered electrodes for carbon steels, FCWs for carbon and stainless steels, consumables for Ni-based alloys, and products for low temperature services as well as high tensile strength steels have long been in demand. KOBELCO opened a representative office in the Middle East in 2014 and began working with local distributors to meet the needs of the region.
KOBELCO’s recent history overseas ---- Europe ----
KOBELCO WELDING OF EUROPE B.V. (KWE) (Figure 25), the production base of FCWs for stainless steels in the Netherlands, celebrated its 20th anniversary in 2015. Since its foundation, KWE has manufactured FCWs for stainless steels and supplied them to European customers and established a reputation for stable and excellent quality. Now, in addition to conventional FCWs for stainless steels, KWE produces such high grade FCWs as [P]DW-2594, for super duplex steel; [P]DW-N625 and [P]DW-N82 for Ni-based alloys; [P]DW-A904L, for high austenitic stainless steels; and [P]DW-310, for fully austenitic stainless steels. A new plant for FCWs for mild steels was added at KWE in 2007 and has gradually expanded its production menu. In addition to conventional FCWs, such as [F]DW-A50 and [F]MX-A100, FCWs for low temperature service, such as [T]DW-A55L, [T]DW-A55LSR and [T]DW-62L have been put into production (Figure 26).

Figure 25: KWE factory appearance

Figure 26: KWE’s product ranges
As energy demand has increased, so has demand for line-pipe installation. KWE has introduced a number of welding consumables developed by KOBELCO that satisfy the needs of construction sites for high efficiency. [T]DW-A70L was developed for API 5L X70 and X80; it is applicable in all position welding and is now being used in a project in Europe. [P]DW-N625P, developed for all position welding of Ni-based alloy pipes, is now being utilized in an undersea project.
KWE established a sales subsidiary company in Sweden in order to expand sales and marketing networks. By listening to European customers who are willing to share advanced technological information, it continues to develop consumables that meet their needs. In other important countries like Germany and Italy, KWE is improving its activities by adding more staff members for sales and marketing.
The high quality [F]LB-52U has long been used for repairing line-pipes in Russia. However, the application of pipes with higher tensile strength grades as well as automated production processes has recently increased. KOBELCO was able to respond to such new line-pipe requirements with [T]LB-62U and applicable FCWs. In Russia, FCWs for stainless steels, consumables for low temperature services like [T]DW-62L and consumables for Cr-Mo heat resistant steels are also in demand.
KOBELCO is determined to develop and supply customer-oriented consumables and technologies in a timely manner in technologically advanced European areas.
KOBELCO’s recent history overseas ---- The Americas ----

Figure 27: KWAI office appearance
KOBELCO WELDING OF AMERICA INC. (KWAI) (Figure 27), the sales company in Houston, Texas celebrated its 25th anniversary in 2015. From there, FCWs for mild steel and stainless steels and solid wires are supplied throughout the USA, Canada and Mexico as well as South America.
For the energy industry, KWAI distributes FCWs for stainless steels and for low temperature service/high tensile strength steels, whereas for the automobile industry, the company offers [F]MG-51T and SE solid wires for car fabrication and [P]MX-A430M (an FCW for 17Cr-Nb type stainless steel) for car exhaust systems. Among some users, interest has been growing for the XR series, FCW’s for stainless steels that are environmentally sound.
Whereas demand for energy in the USA has dropped in comparison with past times, the American construction industry has remained active, and interest in achieving higher efficiency at construction sites has been growing. KOBELCO’s product line-up now includes its robotic welding system. Based on KOBELCO’s confidence that robotic automation would provide the efficiency needed in American construction projects, KWAI opened the ROBOTIC & EQUIPMENT DIVISION, and sales of welding robots and equipment has started. Orders have been taken from several steel frame fabricators.
Responding to American requirements for better seismic design, the company is now developing FCWs that meet seismic design specifications and are suitable for robotic welding. KOBELCO is confident that the development of these products will improve efficiency and contribute to the construction industry’s further progress.

While making continual progress in partnership with local industries around the world, KOBELCO will contribute to develop the respective industries by supporting their Monodzukuri as the most reliable total welding solutions enterprise.
In order to realize this goal, the organization of the head office was changed several times in the past, and now the INTERNATIONAL OPERATIONS DEPARTMENT (IOD) has been reorganized into the GLOBAL OPERATIONS & MARKETING DEPARTMENT (GOMD). GOMD is set in the newly established MARKETING CENTER and has started its activities worldwide.
We are very thankful for your kind patronage of KOBELCO WELDING TODAY as a means of communicating about KOBELCO’s welding technologies. At most of KOBELCO’s overseas locations, exclusive web-sites are available, and some of them are produced in local languages. On the web-site of KOBELCO’s head office, English, Spanish, Portuguese and Russian languages are available. We hope that KOBELCO can contribute to your continual growth and future prosperity.
http://www.kobelco.co.jp/english/welding/>
http://www.kobelco-welding.jp/
THE KOBELCO ARC over the Last Decade:Welding systems and equipment

1.Preface
KOBELCO has supplied a range of robotic welding systems that combine the ARCMAN™ series robots and SENSARC™ power sources since 1980’s, focusing on industries that apply middle to heavy plates such as construction machinery, architectural steel frames, rolling stock and bridges. In this special issue, we look back at what the Welding System Department in the Welding Business has achieved over the last decade and shine a spotlight on the development and commercialization of the welding systems and robotic welding processes that make the best use of KOBELCO’s advantages.
2.Welding procedures for middle-heavy plates
Because middle to heavy plate welding requires high volumes of deposited metals, it follows that the weldments must be of safe and sound quality. KOBELCO’s ARCMAN™ series welding robots meet these requirements with such key and exclusive middle-heavy plate welding functions as sensing and multi-layer welding.
The products and welding technologies developed to solve such issues as reducing arc time and spatter, and maintaining stable and deep penetration are discussed herein.
3.Advancement of tandem-arc welding
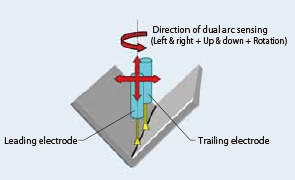
Figure 1: Dual arc sensing function
Tandem-arc welding is a method of achieving sound welds even at faster welding speeds by holding one pool with two electrodes. KOBELCO commercialized a robotic tandem-arc welding system in 2001 and since then has worked to reduce the additional spatter generated by the two electrodes, thereby improving operability and efficiency. In 2008, dual arc sensing was developed, as shown in Figure 1. This function performs dual arc sensing with not only the leading electrode but also the trailing one, thereby ensuring high quality bead shape as well as arc stability.
Additionally, the function to automatically set up welding conditions was developed and installed in the system. The operator now had only to select the codes for groove shape and leg length, and then the optimum welding condition would be extracted from the pre-registered data base and the robot’s operation orbit within the welding section would be automatically generated as well. The subsequent application of advanced robotic tandem-arc welding systems in a number of industries, such as construction machinery, which strives to improve productivity per unit area, has led to significant increases in productivity. Finally, the SENSARC™ AB500, a high quality robotic welding power source, was released in 2010. With its unique control, a stable arc resistant to disturbance could be realized, which minimized arc turbulence as well as spatter generation. Compared with conventional power sources, it can reduce spatter as much as 70% and decrease spatter particle size, too. (Figure 2)
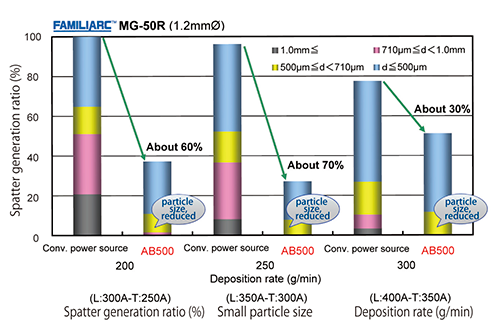
Figure 2: Comparison of spatter particle size and its amount
4.SENSARC™ AB500: a high quality welding power source for robotic welding
SENSARC™ AB500 is a power source for robotic welding that is best suited to medium-heavy plate robotic welding and that has greatly improved welding performance. It produces the best output waveform within each welding mode, such as constant voltage (CV), pulse, and wire diameter and type; it also feeds welding wires at a max. 30 m/minute, which is 20% more than a conventional power source.
1. REGARC™ Process: Low Spatter, Gas Metal Arc Welding Process with CO2 shielding gas (CO2 welding)(2010 ~ )
In conventional CO2 welding with a solid wire, increasing the welding current causes globular and irregular droplet transfer with large particles as well as a remarkable increase in spatter. The REGARC™ Process, however, achieved regular droplet transfer by utilizing pulsed current waveforms to control droplet transfer.
The advantages of this process include extremely low spatter, low fumes and high efficiency. By reducing spatter generation to 1/10 and fume generation to 1/2 in comparison with conventional CO2 welding, the REGARC™ Process improves the work environment and lessens spatter-removing work. Because the process features low heat input and high deposition welding, the mechanical properties of welds are improved. Therefore, in order to make the most of the REGARC™ Process, it was determined that the process should be installed on all robotic welding systems. Beginning in 2010, installation of the process started with the systems for architectural steel frames in the Japanese markets and was gradually expanded to those for column core to column large assembly and completed in 2011 (Figures 3-1 and 3-2). The series of architectural steel frame robotic welding systems are unique to KOBELCO, one-of-a-kind products that continue to be highly reputed by customers. Yet, KOBELCO continues to develop new products and functions in order to contribute to reductions in cost, increases in productivity, and improvements in the quality of architectural steel frame fabrication.

Figure 3-1: ARCMAN™ robotic welding system for column core,installing REGARC™ process

Figure 3-2: Welding system for column large assembly
2. Ultra high current MAG welding process(2012~)
MAG welding with Ar-CO2 mixed gas is an effective welding process that utilizes a high current range to effect spray transfer with small particle droplets and reduce spatter. However, if the current is raised too high, electric resistance may cause the wire tip to overheat, and, in the case of applying solid wires, a so-called rotating arc may be generated. This phenomenon prevented MAG welding with Ar-CO2 mixed gas from increasing efficiency. In response, tandem-arc welding was seen as a desirable solution because two wires could remove the barrier and raise the deposition rate. On the other hand, two electrodes will generate more spatter than a single electrode, and the teaching of a robot with two electrodes is more difficult than one with a single electrode.
An ultra high current MAG welding process has been developed that solves the above problems and achieves a high deposition rate by utilizing an ultra high welding current with a single electrode.
The process applies an exclusive flux cored wire (FCW), [F]MX-A100D, that prevents the FCW from overheating and the FCW’s whole cross section from melting at the same time. It avoids the rotating arc, thereby maintaining spray transfer, even at an ultra high current, and generating extremely low spatter.
This process requires very large currents to achieve maximum effect. It is recommended that two SENSARC™ AB500 power sources are connected in parallel and used as a unit. This setup achieves an extremely high current exceeding 600 ampere and a high deposition rate of nearly 20 kgs/hour, almost equivalent to that of a conventional tandem-arc welding process.
Another feature of the ultra high current MAG welding process is that it offers deep penetration. Because it fulfills the needs of construction machinery fabrication, it is widely applied as a high quality and high efficient welding method.
5.AP-SUPPORT™:Production support software
Launched in 2010, AP-SUPPORT™ is a software product that allows users to visualize a robotic welding system’s operational state. With the ability to monitor the daily operations of ARCMAN™ series robots, they can more easily maintain stable production or make improvements. To be more specific, the program provides accurate and easy-to-understand production control data like the arc generation rate as well as key information in times of trouble.
The program gathers a large amount of the production and welding data that is sent from the robot controller and welding power source through the network into a personal computer as shown in Figure 4. Then, by analyzing and using such production control data as the arc generation rate, moment stops and welding failure, operators can effectively control and make improvements in production.
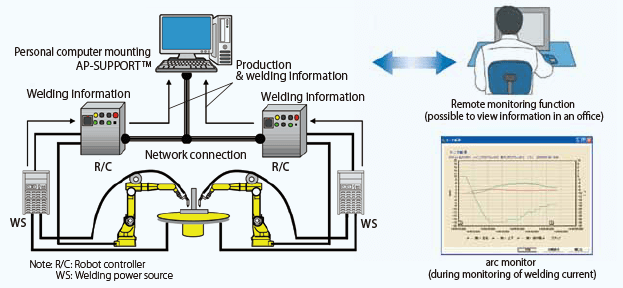
Figure 4: Network connection
It also enables operators to verify the increase or decrease of the arc generation rate and time of the robot’s operation stops. Whereas information related to the location and details of errors once had to be obtained and analyzed manually, AP-SUPPORT™ now allows it to be output automatically, so that it can be accurately understood in a timely manner. The program not only displays real-time data but also secures past welding data, so that when a welding failure occurs, its cause can be investigated by tracing back to the moment the failure occurred.
6.Distinctive robot manipulator
While workpieces continue to increase in size in the field of medium-heavy plate welding, smaller footprints and better space saving are required of robotic systems. KOBELCO has developed two distinctive robot manipulators that meet such needs.
1.ARCMAN™ GS (2010~)
ARCMAN™ GS is an overhead-suspended robotic welding system. It remains in constant demand because it enables an effective approach to large-scale workpieces and saves space. Two features of the ARCMAN™ GS stand out: firstly, the torch cable is installed inside the robot arm in order to prevent interference between the torch cable and the workpiece (Figure 5); and, secondly, wide motion range is achieved due to the overhead suspension.

Figure 5: ARCMAN™ GS with the cable-integrated upper arm
Additionally, the ARCMAN™ GS can mount even tandem-arc welding torches on the 6th axis and take the reverse elbow position, which means the robot’s upper arm can bend behind the robot.
Because the robot approaches a workpiece from above, its motion range is 40% greater than that of the conventional ARCMAN™ MP system, which has an arm size almost the same as that of the ARCMAN™ GS. Thanks to these strong points of the manipulator, KOBELCO’s robotic welding system is small in size, saves space and achieves high productivity per unit area.
2.ARCMAN™ A30S: Ultra small manipulator(2017~)
The shipbuilding industry expects welding automation to reduce manpower and improve productivity and efficiency in fabrication yards. In response, KOBELCO has achieved automating the welding of blocks at hull assembly in shipbuilding, which until recently was not considered feasible. This breakthrough was made possible by developing an ultra small manipulator: the ARCMAN™ A30S and SMART TEACHING™ software. Figures 6-1 and 6-2 show the ARCMAN™ A30S on the robot carry and the welding operation inside the block, respectively.
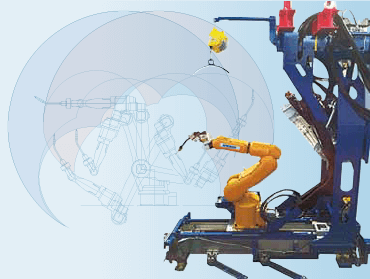
Figure 6-1: ARCMAN™ A30S on the robot carry

Figure 6-2: Actual welding operation with ARCMAN™ A30S at hull assembly
At the block welding stage, every member to be welded, though similar, is so different in sizes and shapes and is arranged in so narrow space that a robot has to be carefully transferred and set, avoiding each member’s interference. Such problems have been solved by combining the ARCMAN™ A30S with the SMART TEACHING™ software.
The software creates the robot teaching program by automatically extracting the welding lines out of the 3D-CAD models used to design the ship. Its effectiveness builds upon KOBELCO’s long experience in welding technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) and Information and Communication Technology (ICT).
7.Postscript
We are determined to contribute to customers’ stable production by enhancing our welding systems, functions and application software in the future as well. And we will continue supplying the robotic welding systems, taking advantage of the position as the total welding solutions enterprise who can supply not only the robotic systems, welding power sources but also the world’s leading welding consumables.
Products
- Main Products
- Welding Consumables
- Arc welding robots
- Industries - Recommended Materials
- Welding Handbook Quick View
- Product Quick View & Highlights
- For HEAT-RESISTANT STEEL
- For STAINLESS STEEL
- For LOW-TEMPERATURE STEEL
- Product Highlight
- Catalog
- Technical Highlights
- Certification
- SDS ※English Only
- ARCMAN
- Welding Robot
- Software






